People usually fall into the emergent need for money when they have to pay their medical bills or children’s tuition fee. The biggest concern at that time is who, and how quickly, will help.
When we need cash but don’t have it, the first thought we usually get is to borrow from someone or somewhere. Today there are many sources, such as personal loans, credit cards, life insurance policies, and others, to borrow money.
Most people look forward to solutions like short-term loans, credit cards, or personal loans. Instead of providing relief, these products often put an additional financial burden on borrowers.
But there is one solution that provides cash in your hands quickly and without deteriorating your financial health. It is nothing but a loan against the life insurance policy.

Use this graphic for free, just source us with this link:
Source Link: https://thefinancesection.com/how-much-can-you-borrow-from-your-life-insurance-policy/
According to the latest Barometer study from LIMRA and Life Happens for the decade 2011 – 2020, the percentage of life insurance policyholders is highest in the year 2020. It not only shows the rising interest of people in life insurance policies but also points towards the possibility that borrowings against life insurance policies might also increase.
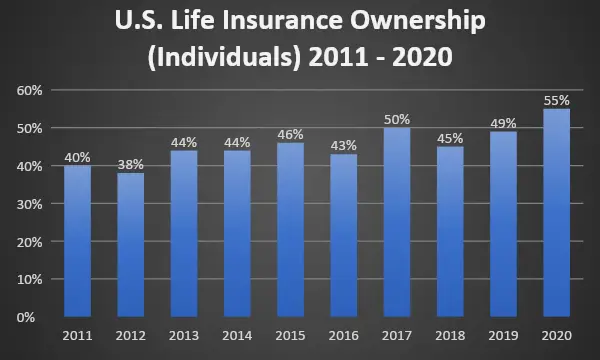
Source: 2020 Insurance Barometer Study, LIMRA and Life Happens
Borrowing Against A Life Insurance Policy
Do you know out of all the available options, a loan against your life insurance policy can be the easiest and quickest way to get cash?
Of course, you must have a life insurance policy in your name if you want to borrow against it. Not many people know, but all types of life insurance products do not allow a policyholder to borrow money. You can borrow if you have a Whole Life Insurance or Permanent Life Insurance policy in your name.
You cannot borrow against Term Life Insurance because no cash value is associated with it, and this kind of insurance is for a limited time only. The period for which a term insurance policy remains in force can be anywhere between one to 30 years.
Borrowing against Whole or Permanent Life Insurance. Why?
If you have a Term Insurance Policy in your name, you won’t get a loan against it. But you can effortlessly borrow money when you have a Whole or Permanent Life Insurance.
It is because of the cash value associated with Whole Life Insurance. When you pay the premium for such a policy, it splits into two parts. One part contributes to the insurance policy’s premium, and another one adds to the cash value.
The cash value functions as a savings account. When cash value investments grow more than the death benefit, the policyholder becomes eligible to borrow against his/ her Life Insurance policy.
Amount You Can Borrow from Your Life Insurance Policy
The amount of money you can borrow from your life insurance policy depends upon the insurer and type of life insurance plan. In most cases, the maximum amount of loan a person can borrow is around 90% of the policy’s cash value. Usually, there are no conditions like you have to borrow at least this amount of money.
When you borrow a loan against your policy, no money gets deducted from the cash value. Your insurance company gives you money and use your policy’s cash value as the collateral. It is advantageous for the policyholder only because the cash value remains a part of your insurance policy and keeps generating interest.
Another advantage of a loan against the life insurance policy is that there are no conditions to repay the loan in a specific duration. Such is not a benefit in other types of loans.
There are a few things you need to know while borrowing this way. They are:
- The interest on your borrowing can be variable or fixed, depending upon your insurer.
- If you fail to repay the annual interest on your loan, it gets added to the outstanding loan’s value. It is not good if that loan lasts for many years because the power of compound interest will increase the loan value significantly.
- If the outstanding loan amount equals the cash value of your insurance policy, it will lapse.
- It is important. If the policy lapses, the policyholder suffers the dual loss. First, loses coverage, and second, need to pay income tax if the outstanding loan amount becomes more than the premiums paid.
The objective of including these points is to help you understand that borrowing against a life insurance policy contains some risks too. It’ll quickly and easily provide cash in your hands, but you need to be careful about the size of the loan amount. Also, be consistent in paying interest.
How to Borrow Against A Life Insurance Policy?
Insurance companies have simplified borrowing against a life insurance policy. Your insurer will ask you to fill a form, and you’ll find the money deposited in your account within the next few days.
Your insurer might also ask you to provide certain documents with your application. For example, a copy of your identity card, address proof, etc. Your insurance company may also ask to provide a signed confirmation document or confirmation from notary if:
- The loan amount is beyond a specific limit (for example, more than $50,000).
- You have recently made changes to your account and informed your insurer about it.
- The policy recently went through a change in ownership.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Loan Against Life Insurance
When it comes to borrowing, you may get help from many instruments such as personal loans, credit cards, life insurance policy, etc. Like every other loan product, life insurance loan also has some advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s have a look at them:
Advantages of Loan Against Life Insurance Policy
- If the cash value is sufficient, you won’t be asked any questions.
- Unlike banks, the borrowing process is quite simple. The insurer will ask you to fill a form before sanctioning the loan.
- Credit card borrowings show up on the credit report, but cash-value/ life insurance policy loans don’t.
- The interest rate charged on borrowing against life insurance is low in comparison to the personal loan or credit card debt.
- There is no time limit to repay the loan. You may repay it as per your convenience.
- It may sound surprising, but there is no obligation to repay the loan borrowed against a life insurance policy. It doesn’t mean the insurer will forget your debt. Not repaying the outstanding loan amount affects the policyholder in many other ways.
Disadvantages of Loan Against Life Insurance Policy
- A life insurance policy loan is given when cash value becomes more than the death benefit. It may take years for the cash value to grow this big. If you are expecting to borrow within the first few years of buying the insurance policy, you may receive only disappointment.
- If you do not repay the outstanding loan amount throughout your life, the payout or death benefit on your policy will decrease.
- You should pay the interest on your loan regularly, otherwise, it will add against the cash value. When compounded, it’ll hurt more.
- When the loan amount plus the interest on it exceeds the cash value, the policy often lapses.
- You may be taxed if the policy lapses because of not repaying the loan. This tax is levied if some amount remains unpaid even after the policy lapses.
How to Repay a Loan Taken Against Life Insurance Policy?
Loan against a life insurance policy is quite different from other types of borrowings. The policyholder is at an advantage not only while borrowing but also while repaying the outstanding amount.
It gives so much freedom that you don’t even need to worry about repaying the loan. It doesn’t mean you should avoid repaying the borrowed amount. A policyholder shouldn’t worry about the loan amount or the annual interest until the total outstanding borrowing remains below the cash value of a life insurance policy.
Once the total borrowing (including the annual interest) exceeds the cash value of your policy, your policy might lapse. Your beneficiary won’t get the death benefit.
So, what should be the right way to repay the loan?
The right way to repay the borrowing against a life insurance policy is to pay it back on time. Whether interest or the borrowed amount, repay it at regular intervals.
Do not allow the interest to grow so much that repaying the loan becomes almost impossible. The same applies for the loan amount. If you don’t repay it regularly and die before clearing your dues, your beneficiary won’t get the actual death benefit. The amount they receive will be the balance remaining after deducting the outstanding amount.
Frequently Asked Questions
The information available in this article clarifies a lot of things about borrowing from your life insurance policy. However, some questions might still be on your mind. Let’s see if answers to these frequently asked questions also satisfy the queries emerging in your mind.
1. I have a term life insurance policy of 30 years. Can I borrow against it?
The borrowing against a life insurance policy doesn’t depend on the policy’s tenure. The policy’s cash value is the deciding factor.
Since a term life insurance policy does not have a cash value, a policyholder is not allowed to borrow against it.
2. How soon a policyholder becomes eligible to borrow against a life insurance policy?
A policyholder becomes eligible to get a loan against his or her life insurance policy whenever the policy’s cash value grows enough to satisfy the borrowing needs. In the case of whole life insurance policies, it might take many years for the sufficient growth of cash value.
There are certain types of policies that allow borrowing within a few months. To learn about them, you should consult your insurance advisor. The availability of such options doesn’t mean you should borrow as soon as you become eligible. Take a loan only if you want it, otherwise not.
3. Is it necessary to pay off the loan taken against the life insurance policy?
It is not mandatory, but you should effectively repay your borrowing. Here are some reasons why you should do that:
- When you pay off this debt, you have the option to borrow for the fulfillment of other needs. For example, if you repay the loan taken to cover the medical expenses, you can again borrow to fulfill your retirement needs.
- If you clear this loan, your beneficiaries will get the entire death benefit when you die. If you don’t repay, the outstanding amount gets deducted from the death benefit.
- When the total outstanding amount reaches or exceeds the cash value, your policy may lapse. In this case, the remaining debt is taxable.
So it is best to repay the loan. However, many people borrowing to fulfill the after-retirement expenses decide not to repay the loan.
Your insurance advisor might suggest you wisely in this matter.
4. Which documents do I need to submit to get a loan against my policy?
An advantage while borrowing against your policy is that minimum or no documents are required. Of course, you need to fill and submit the loan request form. If your insurance company asks for submitting documents, it may ask for the original life insurance policy, ID proof, address proof, latest photograph, etc.
5. Loan against a life insurance policy attracts tax. Is it true?
In general, borrowing against a life insurance policy is tax-free. However, you may face tax implications if your policy lapses because of the outstanding amount exceeding cash value.
Final Words
A Life Insurance policy provides multiple benefits. People purchase this insurance product to cover the financial risks associated with their death. But, the real surprise comes when they realize that their policy is an easy and quick way to borrow money.
One mistake most borrowers make is to ignore repaying the loan. You should be consistent in the repayment of your outstanding amount. Missing or not repaying the loan borrowed against your life insurance policy will not be fruitful for you, your family, or your beneficiaries. You can also consult your insurance advisor for a piece of wiser advice on this.

